Data breaches are the most common security threats in the contemporary age that can create significant challenges at individual and commercial levels. To mitigate such risks, experts and companies often adopt data encryption methods, such as symmetric and asymmetric encryption. These tactics protect data from unauthorized access, sustaining robust security measures.
Encryption is a process to shield datasets and information with specific keys. Sources reflect that in most countries, more than 90% of web traffic is encrypted or encoded for security purposes. However, only 27% of companies incorporate encoding methods. It is also crucial to mention that one of the key reasons for data loss nowadays is a lack of appropriate safety initiatives like data encryption.
This blog shall give an overview of symmetrical encryption alongside shedding light on how it works and leading use cases.
What is Symmetric Encryption?
As a type of data encryption, symmetric encoding tactics or symmetric key cryptography refers to the process that uses the same password to lock and unlock datasets. Generally, the method of encryption masks confidential data with keys to keep them protected from unwanted risks. These keys are used twice in the whole activity — initially when encrypting or locking data and when decrypting or unlocking it.
In symmetric encryption, the same password can be used to lock and unlock datasets. Meanwhile, in asymmetric encryption, users leverage dissimilar keys for data locking and unlocking purposes. Keeping the same passwords reduces complexities in accessing and managing data effectively. Some of the specimens for symmetric key formulas are AES, DES, Blowfish, RC4, etc.
Experts consider symmetric-key cryptography a weaker method of encryption as it involves sensitive password-sharing stages. In case of any vulnerability, cyber-attackers can easily access and steal the keys, alongside retrieving confidential information from datasets. Considering such risks, many companies do not prefer to incorporate symmetric methods of encryption.
There are certain advantages to adopting symmetric-key cryptography, such as limited complexity and cost efficiency.
How Does Symmetric Encryption Work?
Data encryption is a methodology for safeguarding sensitive information with passwords. Hence, the process commences with determining the passkeys. These keys do not follow any structure or form; they can be random numbers, letters, symbols, or a combination of all. Following this, the original data and the password are transferred into encryption algorithms, where the former becomes ciphertext from plaintext. There are two broad cipher categories in symmetric encryption:
Block: Here, similar-sized blocks are used to lock data, and this is also known as an Advanced Encryption Standard.
Stream: This system locks data bit by bit through real-time data optimization.
While briefing the whole process, we can state that primarily, data is created or stored by a source who intends to share the information with another party. The primary source uses a symmetric key to encrypt datasets, following which an extra shield of protection is added to sensitive information using encryption codes of either blocks or stream. The receiver receives the data in an encrypted version, which requires the symmetric code to get decrypted.
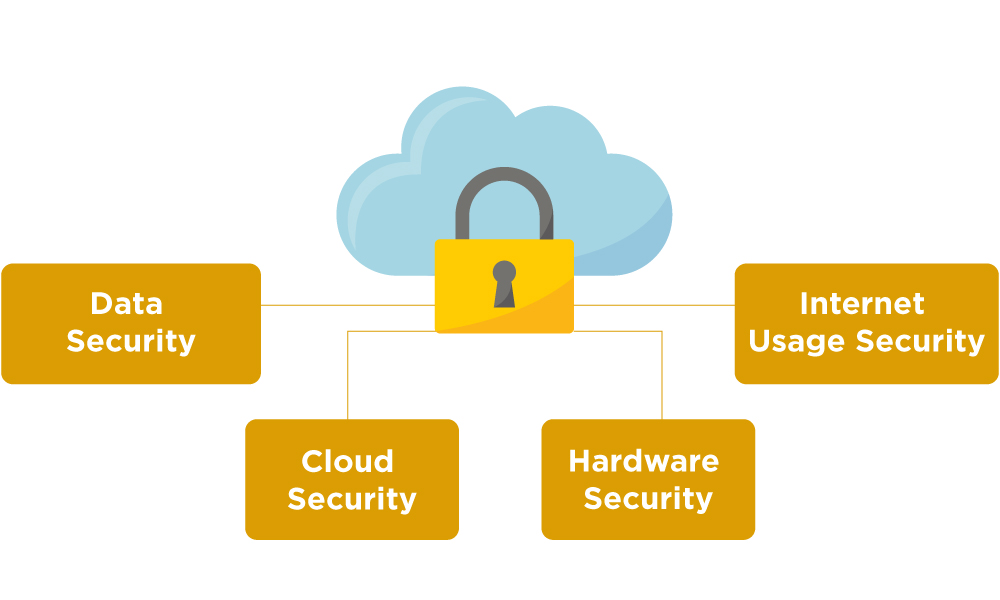
Use-Cases of Symmetric-key Encryption:
Symmetric encryption can be useful in multiple domains, starting from cloud security to safer internet usage. Let us discuss a few use cases for the same:
Data Security:
Symmetric key cryptography protects small and large amounts of data from threats and unwanted access. When datasets are encrypted with a secret code, it won’t be possible for anyone to access them and retrieve information without knowing the key.
Cloud Security:
Cloud computing is a common tech trend in current times, and it is vulnerable to cyber threats. Symmetric encryption, in this regard, can be remarkably beneficial for cloud providers and organizations integrating cloud.
Hardware Security:
Hardware is often at risk alongside software. Therefore, protecting them is equally crucial. Symmetric key cryptography can be beneficial for this purpose. So, when installing hardware, users need to use the symmetric keys to decrypt and utilize it.
Internet Usage Security:
Symmetric encryption can safeguard internet browsing and interaction over social media platforms.
Concluding Remarks!
Symmetric encryption is one of the most convenient and budget-friendly tactics to protect data from threats. Nevertheless, this method has certain limitations, such as the requirement for meticulous key sharing. Therefore, we recommend not overlooking any shortcomings in your effort to safeguard sensitive data.
Read our other informative blogs and keep up with the cybersecurity spectrum!
Also read:
Data Encryption Software: Your Ultimate Guide
What Do You Mean By Remote Network Security?





