Imagine a system where you can control your digital identities without depending on any authority. Well, this is possible through the DID systems.
Research indicates that the global decentralized identity market will record a 90.3% CAGR from 2023 to 2030. In the digital age, people have their identities fragmented across various online platforms, and their personal data is stored in silos controlled by entities such as governments or companies, leading to challenges.
The challenges pertain to privacy violation, identity theft, and an inherent lack of user control over one's digital footprint. The paradigm of decentralized identity provides a groundbreaking method of addressing these challenges by reformulating how the process of special identity creation, management, and verification.
Decentralized identity reclaims the control of personal data to individuals. Users manage their identity information that leads to more private and secure digital interactions. As a result, administrative chores will be less on institutions that handle many identity databases.
What is Decentralized Identity System?
A decentralized identity (DID) system is a technological framework that allows entities to create, own, and manage their digital identities without depending on a central authority. These systems leverage distributed ledger technology, cryptographic protocols, and verifiable credentials to institute trust between parties while also preserving privacy.
The architecture consists of three main parts: identity holders who have and manage their credentials, issuers who generate and authenticate verifiable claims, and verifiers who assess the legitimacy of those claims. These systems reflect the principles of self-sovereign identity through digital wallets, which store decentralized identifiers and verifiable credentials.
The credentials contain cryptographically signed attestations, while the DID system serves as unique identifiers registered on distributed ledgers. This replaces traditional username/password systems with challenge-response authentication protocols based on public-key cryptography. Users can selectively disclose only the necessary information while maintaining cryptographic proof of data integrity and provenance.
Key Technologies Powering DID Systems
Distributed ledger technologies form the backbone of modern decentralized identity frameworks. These immutable databases provide the essential trust layer for DID systems by recording public keys and schema definitions without storing personal data. Blockchain-based implementations offer transparency and resistance to tampering.
Newer DID system variants explore directed acyclic graphs and other consensus mechanisms that reduce environmental impact while maintaining security properties. Public key cryptography enables secure ownership and control in the decentralized identity ecosystem.
Users generate private-public key pairs, where the private key remains exclusively in their possession while the public component becomes part of their DID system registration. This cryptographic foundation allows for digital signatures that prove control over identifiers without revealing the underlying secrets, creating a robust technical basis for authentication without centralized password databases.
How does Decentralized Identity Strengthen User Control and Privacy?
Decentralized identity is shaking up the old way we think about data ownership by putting individuals front and center in their digital lives. Instead of handing over personal information to big corporate databases—where it’s at risk of breaches and exploitation—users of Decentralized Identity (DID) systems keep their credentials safe in secure digital wallets.
The idea of minimal disclosure that DID systems promote is a big leap forward for privacy protection. In the past, verifying your identity often meant sharing way more information than necessary—like showing your driver’s license to prove your age, which also reveals your address and license number. With decentralized systems, users can create "proofs" that answer specific questions without exposing all that extra data.
Perhaps the most exciting aspect of DID systems is the level of transparency and consent they bring to identity management. Users get cryptographically verifiable records showing who asked for access to their information and when creating a clear trail of identity interactions. The new approach respects regulatory principles like data minimization while going beyond them.
Use Cases and Benefits Across Industries:
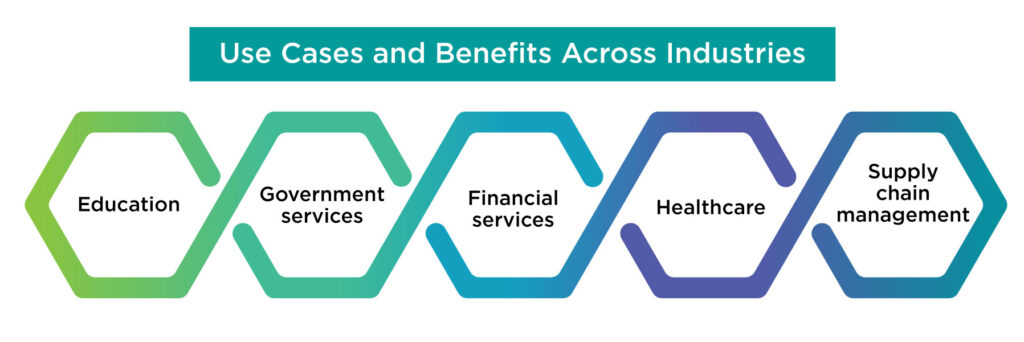
Education
Diplomas, certificates, and professional credentials can be issued as verifiable digital assets within a DID system, eliminating document forgery concerns while simplifying verification for employers.
Government services
Government services all over the world are using DID systems to modernize citizen identification and service delivery. Citizens can interact with government agencies by using cryptographically secured digital credentials. This reduces bureaucratic friction while enhancing security.
Financial services
A DID system can be implemented particularly for customer onboarding and fraud prevention. With decentralized identity, consumers can reuse verified credentials across financial providers, streamlining account creation while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Healthcare
DID systems enable patients to maintain portable health credentials that can be selectively shared with specialists, emergency providers, or research initiatives. This approach reduces administrative overhead while enhancing privacy—patients can prove vaccination status or medication allergies without exposing their complete medical history.
Supply chain management
Supply chain management represents another domain where decentralized identity principles deliver substantial value. Traditional supply chains struggle with provenance verification and counterfeiting issues across complex international networks.
Challenges and the Future of Decentralized Identity
Even though decentralized identity has a strong potential, there are some consequential hurdles that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted. One of the biggest hurdles here is the technical complexity. Many existing DID systems demand a level of expertise that most regular users simply don’t possess.
To bridge this usability gap, we need to create more intuitive interfaces that can simplify the cryptographic details while still keeping everything secure. On top of that, the existing regulatory frameworks that were designed for centralized identity management add a layer of uncertainty regarding compliance with decentralized methods.
Organizations are understandably cautious about adopting solutions that might clash with regulations like GDPR or struggle with recognition across borders. These hurdles, along with the network effect challenge—where the value of a system grows only as more people use it—have made it tough to move from promising pilot projects to actual mainstream use.
Contemplating the Future of DID Systems!
Looking ahead, it seems like decentralized identity is more likely to be gradually woven into our digital infrastructure rather than causing an immediate upheaval. We can expect early adoption to continue in specific high-value scenarios where there are clear cost savings or compliance benefits. As standards develop and regulations become clearer, DID systems are set to act as a bridge between traditional identity providers and digital services.
For more informational content, keep visiting us at SecureITWorld.
Also Read:
How to Protect Your Digital Identity Online? The Best Practices
How Secure is Automotive Digital Identity?