Identity and authentication management is one of the most impactful methods for sustaining robust security. The process keeps data away from illegal access and vulnerabilities that can threaten individuals and organizations. Single sign-on, or SSO, is a common practice for implementing user authentication management.
According to sources, 80% of cyberattacks around the globe are an outcome of identity-based violations. The same number of cases are caused by tracking and stealing weaker passwords. Such incidents are a threat to companies of all sizes. To address such risks, companies adopt several security tactics, among which single sign-on is significant.
Let us scrutinize the method of single sign-on in this blog alongside discussing its working, benefits and comprehending whether it is really safe.
What is SSO?
Single sign-on is a security measure that businesses usually employ to manage users who access organizational data and applications. It is a simple method to authenticate users to access and use company assets. The process limits the requirement of setting multiple pass keys for different applications and having weak passwords.
Remote and hybrid work cultures are among the principal causes for the increased implementation of single sign-on lately. With reduced risks of illegal access, this security tactic eliminates complex access management practices.
While authorizing users, single sign-on seeks for SSO token. Such tokens are nothing but credentials that allow individuals to validate their identity proof and access the tools they want. There are several classifications of single sign-on, including Open Authorization or OAuth, Security Access Markup Language or SAML, Kerboros, and OpenID Connect or OIDC.
How Does SSO Work?
Single sign-on requires an identity provider (IdP) system that runs on the same server as other tools and applications that a company uses. It simplifies the process of user identity verification. The server accordingly identifies individuals who are permitted to access the tools and share encrypted credentials or tokens with them.
By using the credentials and specific log-in IDs, individuals access the applications that are authorized by their companies. The process eliminates the requirement for initiating multiple access requests for different software. Therefore, users can leverage every application once they process through SSO.
Advantages of Employing Single Sign-On:
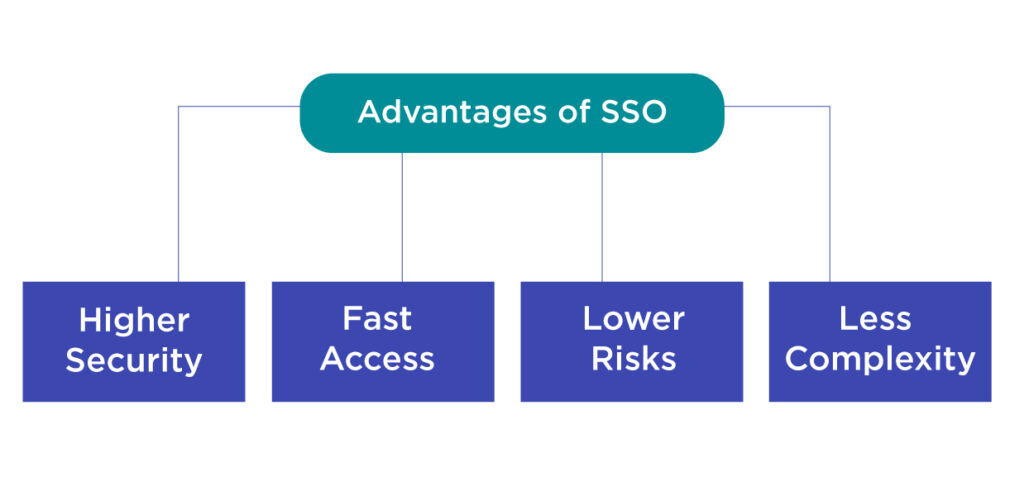
Higher Security:
Single sign-on strengthens security frameworks in organizations, enabling robust authentication methods. The credentials or security tokens SSO requires are unique every time for every user. Hence, there are limited opportunities for unauthorized access and data breaches.
Fast Access:
The security tactic simplifies and makes the application usability process quicker. So, users can access and use several applications at a time without encountering significant delays.
Lower Risks:
Solid authentication frameworks allow companies to operate in a risk-free environment, eliminating the potentiality of major security threats. Additionally, it limits the risks related to third-party security service providers.
Less Complexity:
Protective methods in organizations are usually complicated for users as they include multiple phases. Nevertheless, single sign-on can be essential in this regard, enhancing user experience and sustaining effective security practices.
Is Single Sign-On Safe?
Though SSO offers promising methods to solidify security, it also has certain limitations. Thus, we can state that the process is beneficial yet is not 100% safe for companies. It is important for users to continuously monitor the strategy to get the best security outcomes. Below are some of the limitations to consider before the implementation of single sign-on:
Credential sensitivity: Single sign-on initiates one password to access multiple applications at a time. Therefore, if the credentials are weak or get stolen, major challenges can take place. It can also be a reason for insider threats in organizations.
Over-reliance on SSO systems: The whole process of single sign-on highly depends on SSO systems. So, in case of any disruption in the systems, users can face difficulties accessing required applications.
Compatibility with all applications: Single password verification tactics for multiple software can be ineffective if the applications are not compatible with the systems.
Concluding Remarks:
The increasing number of cyber-attacks indicates the urgent need to strengthen organizational security practices. In this regard, single sign-on can be a key strategy. The method is one of the most preferred tactics by professionals to safeguard their IT infrastructure. SSO requires continuous configuration and standardization while toughening protective measures in companies. For this purpose, considering its implementation challenges is crucial.
Find more informative blogs and articles on SecureITWorld!